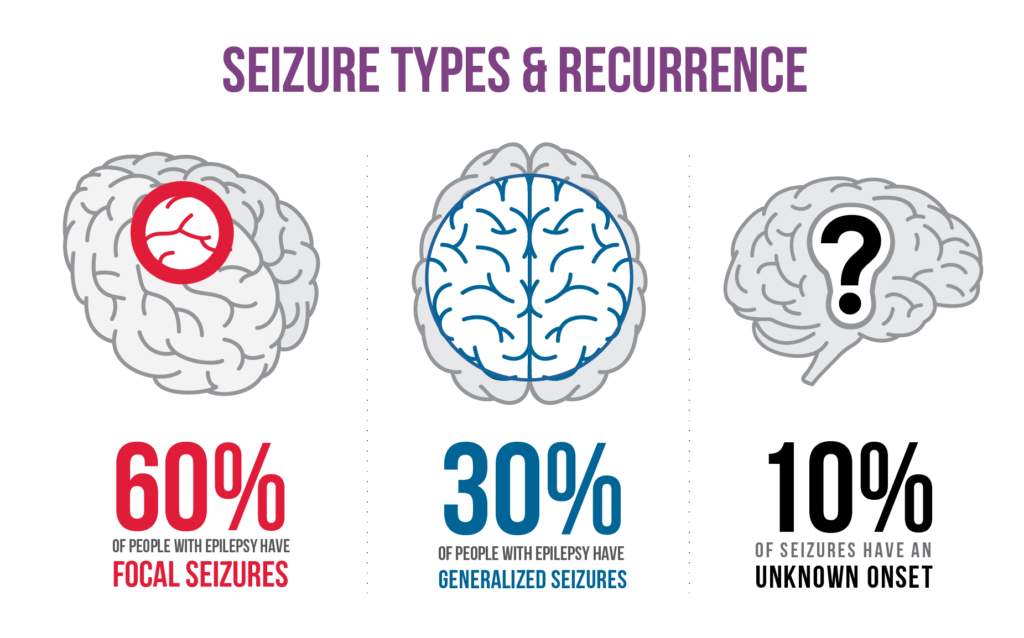
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects approximately 1% of women of reproductive age. Women with epilepsy face unique challenges during pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum, as epilepsy is considered a high-risk condition for pregnancy. In this essay, we will discuss the impact of epilepsy on pregnancy, the potential risks associated with epilepsy during pregnancy, and the management and treatment options available for pregnant women with epilepsy.
Impact of epilepsy on pregnancy:
Epilepsy can affect pregnancy in several ways. Women with epilepsy may experience more seizures during pregnancy, which can pose a risk to the health of the mother and the developing fetus. Seizures can lead to falls, trauma, and injuries, which can be especially dangerous during pregnancy. In addition, seizures during pregnancy can cause oxygen deprivation to the fetus, which can lead to developmental delays or other complications.
Women with epilepsy may also experience changes in seizure patterns during pregnancy. Some women may experience a decrease in seizures, while others may experience an increase. The reasons for these changes are not fully understood, but they may be related to hormonal changes or alterations in medication dosages.
Epilepsy medications can also affect pregnancy. Some anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) have been associated with an increased risk of birth defects and other complications. However, it is important to note that the risks associated with AEDs must be weighed against the risks of uncontrolled seizures during pregnancy. Seizures during pregnancy can pose a greater risk to the developing fetus than the potential risks associated with AEDs.
Potential risks associated with epilepsy during pregnancy:
Women with epilepsy face several potential risks during pregnancy. These risks include:
- Increased risk of seizures: As mentioned earlier, women with epilepsy may experience more seizures during pregnancy, which can pose a risk to both the mother and the fetus.
- Obstetric complications: Women with epilepsy may be at an increased risk of certain obstetric complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature labor, and fetal distress.
- Medication-related risks: Some AEDs have been associated with an increased risk of birth defects and other complications.
- Developmental delays: Seizures during pregnancy can cause oxygen deprivation to the fetus, which can lead to developmental delays.
- Increased risk of maternal mortality: Women with epilepsy may be at an increased risk of maternal mortality during pregnancy and delivery.
Management and treatment options for pregnant women with epilepsy:
Managing epilepsy during pregnancy requires a collaborative approach between the obstetrician, neurologist, and epilepsy specialist. The goal of treatment is to control seizures while minimizing the risks associated with medication use during pregnancy.
- Pre-conception counseling: Women with epilepsy who are considering pregnancy should receive pre-conception counseling to discuss their medication regimen and potential risks associated with pregnancy.
- Medication management: Women with epilepsy may need to adjust their medication dosages during pregnancy to maintain seizure control. AEDs that are known to be safe during pregnancy should be used whenever possible.
- Monitoring: Pregnant women with epilepsy should be closely monitored throughout pregnancy and delivery. This may include regular fetal monitoring, ultrasound exams, and seizure monitoring.
- Delivery planning: Women with epilepsy may require special delivery planning, including consideration of the use of anesthesia and monitoring for seizures during delivery.
- Postpartum care: Women with epilepsy should receive postpartum care that includes monitoring for seizure activity and adjustment of medication dosages as needed.
Conclusion:
Epilepsy is considered a high-risk condition for pregnancy. Women with epilepsy face unique challenges during pregnancy, including an increased risk of seizures, obstetric complications, and medication-related risks. However, with appropriate management and treatment, most women with epilepsy can have a successful pregnancy and delivery. It is important for pregnant women with epilepsy to work closely with their obstetric